Posters
Posters
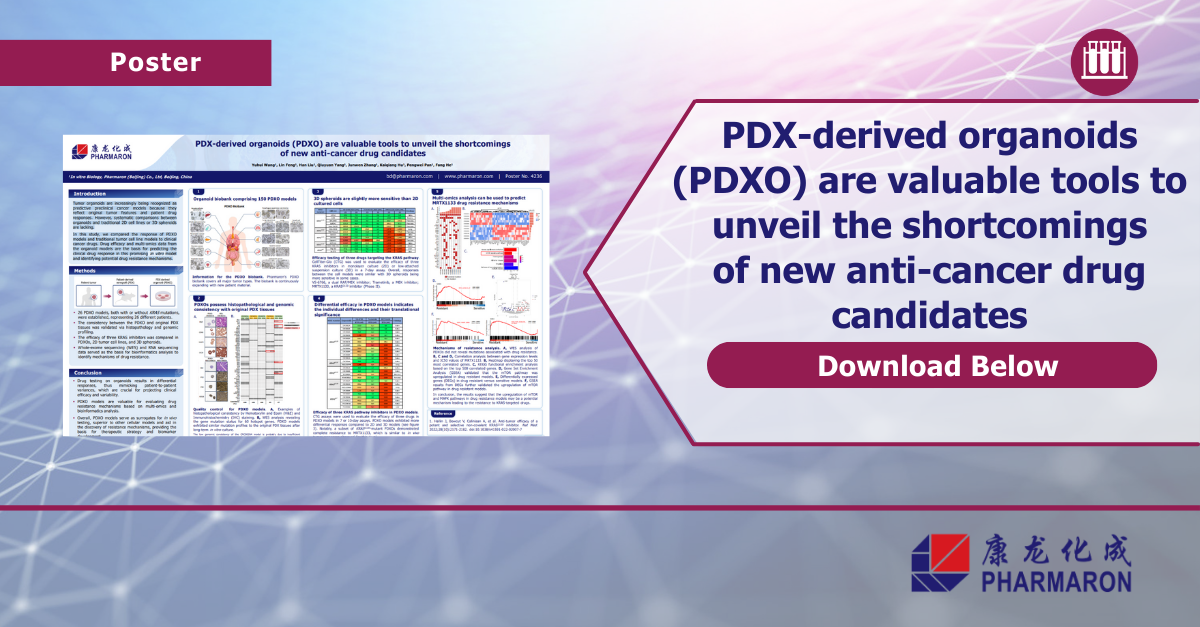
PDX-derived organoids (PDXO) are valuable tools to unveil the shortcomings of new anti-cancer drug candidates
Tumor organoids are increasingly being recognized as predictive preclinical cancer models because they reflect original tumor features and patient drug…
Posters
A multifaceted study of X-Ray radiation therapy across diverse mouse tumor models
Although radiation contributes to approximately 40% of all cancer treatment regimens globally, preclinical programs to evaluate its capacity in combination…
Posters
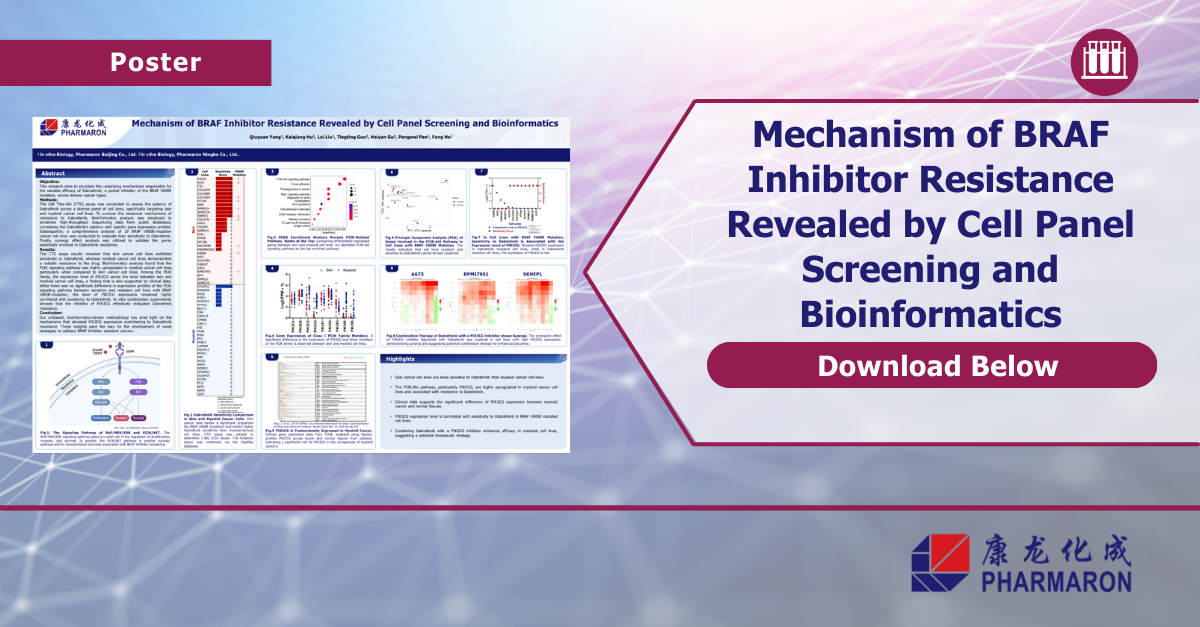
Mechanism of BRAF Inhibitor Resistance Revealed by Cell Panel Screening and Bioinformatics
This research aims to elucidate the underlying mechanisms responsible for the variable efficacy of Dabrafenib, a potent inhibitor of the…
Posters
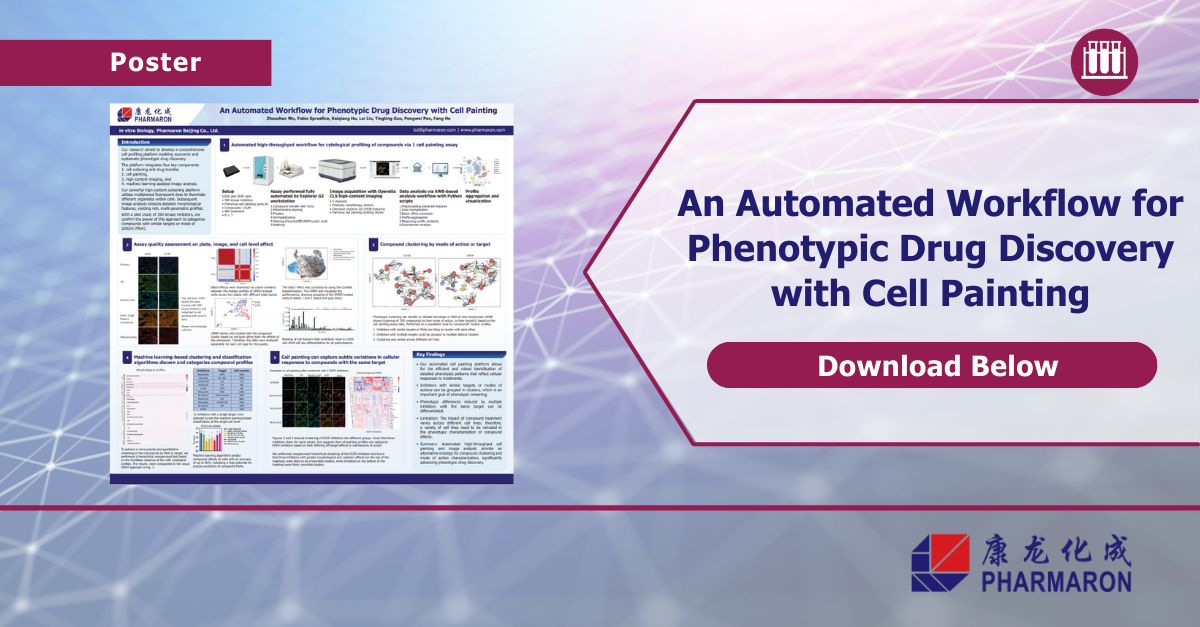
An Automated Workflow for Phenotypic Drug Discovery with Cell Painting
Learn more about how our powerful high-content screening platformutilizes multiplexed fluorescent dyes to illuminatedifferent organelles within cells.
Posters
Permeability Assay Platform by Using Stably Transfected MDCKII-canine MDR1 KO Cells with P-glycoprotein from Different Species
Stay up-to-date on the FDA’s newest recommendations for drug metabolism, drug transporters, and protein binding with the 6th edition of our Drug Metabolism and Transporter…